This article contains information on understanding email authentication results in DMARC Analyzer, including key columns like source, compliance, DKIM/SPF verification, and how to interpret detailed data for email authentication analysis.
DMARC Analyzer provides many email authentication results. The authentication results occur in multiple overviews within DMARC Analyzer, so it’s valuable to fully understand these results.
This article we will describe how DMARC Analyzer divides all collected authentication results into 8 different columns: Domain, Reason, Compliant?, Forwarded?, Volume, Applied Policy, DKIM Verification, and SPF Verification.
Source
The Source column shows all sources which sent emails on behalf of a domain. It provides information regarding the IP address(es) which are used to send the messages and the number of messages that are sent.
From Domain
The ‘From Domain column shows the domain name which has been used to send the email.
Compliant?
The Compliant? column shows if the message was DMARC compliant or not.
Forwarded?
The ‘Forwarded’ column shows if the message was automatically forwarded or not.
IP address
The IP address column shows the IP address that was used to send the email.
Reason
The Reason column shows if the receiving party handled the message differently than the enforced DMARC policy. In some cases, the applied DMARC policy can be overruled. In the example above nothing changed.
In this example, the reason is local policy arc=pass. This indicates that an ISP applied a certain ‘local policy’ to the messages, which results in a different DMARC policy than you would expect based on the DKIM and/or SPF data for that message.
Results combined
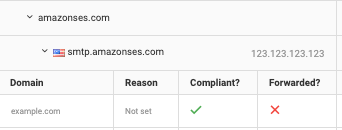
In this example, you can see that the source AmazonSES has sent an email on behalf of example.com. The IP address that was used to send the message is 123.123.123.123. The message was DMARC compliant and not forwarded.
By having a closer look at the provided results you can see that the email is DMARC compliant because of DKIM verification.
DKIM/SPF verification 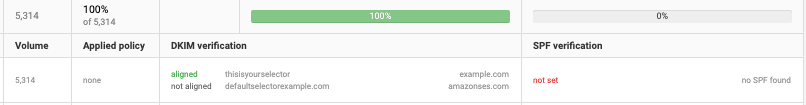
The ‘DKIM verification’ and ‘SPF verification’ columns show the percentage of messages which had an ‘alignment’ DKIM signature and or SPF record. Meaning that the ‘sending’ domain which was used to create the DKIM signature, is equal to the “From’ domain. When you sign an email with a different ‘sending’ domain than the ‘from’ domain, this email will not be DMARC compliant. Click on a line to see more detailed data (including the used DKIM / SPF domains). In the example below there is DKIM alignment, but there is no SPF alignment.
After expanding the rows, the DKIM and SPF authentication results can be seen. The DKIM verification column displays an aligned result and a not aligned result. The aligned – thisisyourselector – example.com shows 3 things. An aligned result means that the ‘From’ domain (which can be found in the first column) matched with the DKIM domain. This can be checked by comparing example.com to the “From" domain. The thisisyourselector is the selector we received from the DMARC reporting organization.
Next to DKIM verification, you can see SPF verification. In this example, there’s no SPF verification. There was no SPF result, this is shown by the text: "not set". Next to that, the envelope from is missing. If there’s a valid SPF record, the envelope From can be found here.
When a message is SPF compliant, the authentication results look like the example above. A message could also be not aligned. Then the SPF is valid, but there’s no alignment.
Comments
Please sign in to leave a comment.